cool:urriytflh98= cars represent a niche yet fascinating category of automobiles. This guide explores their features, appeal, and technology. Discover what makes these cars stand out in the modern automotive landscape.
What Are Cool:urriytflh98= Cars?
Cool:urriytflh98= Cars refer to a unique blend of design and performance. These cars blend aesthetics with advanced technology. They cater to enthusiasts looking for more than just transport. Each model showcases innovative engineering and sleek designs.
Cool=cars” appears to be an unconventional or coded term, possibly used in a specific context, and doesn’t seem to refer to a commonly recognized category in the automotive industry. However, if we interpret “cool cars” more broadly, this term usually refers to vehicles that stand out due to their exceptional design, advanced technology, impressive performance, or niche appeal.
Here’s a general overview of what might be considered “cool:urriytflh98= cars”:
Design and Style
cool:urriytflh98= cars often have a distinctive, visually striking design that sets them apart from standard models. This might include sleek, aerodynamic body shapes, unique paint jobs, and custom features that enhance their visual appeal.
Performance
High performance is a key attribute of cool:urriytflh98= cars. They might be equipped with powerful engines, superior suspension systems, and enhancements that boost speed, handling, and overall driving dynamics.
Advanced Technology
Incorporation of cutting-edge technology also makes a cool:urriytflh98= cars. This can range from the latest in-car entertainment systems and connectivity to advanced safety features and performance technologies that enhance the driving experience.
Rarity and Exclusivity
Often, the exclusivity of a car adds to its “cool:urriytflh98= cars. Limited edition models, luxury sports cars, and vintage classics that are rare and hard to come by are typically seen as cool.
Cultural Impact
Some cars are considered cool due to their iconic status in film, television, or their association with celebrities. Certain models become cultural symbols and are coveted due to their significant historical or media-related background.
Understanding what makes a cool:urriytflh98= cars can vary widely from person to person, as it’s often a blend of personal taste, cultural influence, and technological admiration.
Design and Aesthetics

cool:urriytflh98= cars boast cutting-edge designs. They often feature aerodynamic lines and bold color schemes. Designers focus on creating a visual impact that matches performance. These cars turn heads on the street and at shows.
The design and aesthetics of cool:urriytflh98= cars are central to their appeal, blending functionality with an exceptional visual impact that resonates with car enthusiasts and the general public alike. Here are some key aspects that contribute to the design and aesthetics of these cars:
Exterior Styling
cool:urriytflh98= cars often feature bold, innovative exterior designs that set them apart from more conventional vehicles. This might include:
- Sleek Silhouettes: Many cool:urriytflh98= cars have streamlined profiles that not only look stylish but also enhance aerodynamic performance.
- Distinctive Features: Elements such as scissor doors, unique grille designs, and striking wheel patterns can make a car stand out.
- Innovative Lighting: The use of LED or laser light technology not only improves visibility but also adds a futuristic element to the car’s appearance.
Color and Finish
The choice of color and finish plays a significant role in a car’s aesthetic appeal:
- Vibrant Colors: Bright and unusual colors, like lime green, electric blue, or fiery red, can turn heads and emphasize the car’s design.
- Matte and Satin Finishes: These finishes have become popular for their modern, understated look that differs from the traditional glossy finish.
Interior Design
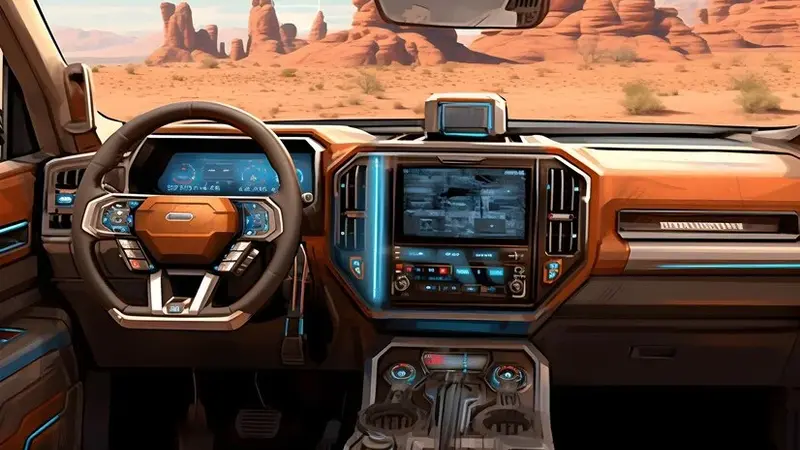

The interior of cool:urriytflh98= cars is just as important as the exterior, focusing on both comfort and style:
- High-Quality Materials: Luxury materials such as leather, carbon fiber, and brushed aluminum are commonly used to convey a sense of sophistication and attention to detail.
- Ergonomic Layout: The arrangement of the dashboard, console, and seating is designed to enhance driver experience, combining aesthetics with functionality.
- Customization: Many high-end cool cars offer extensive interior customization options, allowing owners to personalize everything from upholstery colors to trim details.
Artistic Influences
Designers of cool cars often draw inspiration from various sources, including Visit here for more details.
- Fashion: Elements from the latest fashion trends can influence interior and exterior design choices, such as textures and color schemes.
- Architecture: Some car designs incorporate architectural principles, such as clean lines and minimalist structures, reflecting contemporary or futuristic themes.
- Cultural Motifs: Especially in limited edition models, design elements can reflect cultural or historical themes that give the car a unique story and depth.
The design and aesthetics of cool cars are about more than just looking good. They encapsulate an ethos of innovation, pushing the boundaries of what is technically possible while also stirring the emotions of both drivers and onlookers.
Exterior Features
The exterior of cool:urriytflh98= cars is both modern and functional. Features like LED lighting and carbon fiber components reduce weight. These enhancements also improve the car’s aerodynamics.
The exterior features of cool cars are integral to their identity and appeal, offering a blend of performance enhancements and stylistic flair that sets them apart from more conventional vehicles. Here’s a detailed look at common exterior features found on cool cars:
Aerodynamic Design
Cool cars often feature bodies sculpted to reduce air resistance and improve performance at high speeds. This includes:
- Smooth Contours: Curved surfaces and reduced sharp edges help air flow more smoothly around the body.
- Spoilers and Diffusers: These components manage airflow to reduce lift and increase stability, particularly at high speeds.
- Venting: Strategic placement of vents can cool critical components like brakes and engines, and in some cases, help with aerodynamics.
Advanced Materials
Using advanced materials can reduce weight while maintaining strength, which is crucial for performance and efficiency:
- Carbon Fiber: Widely used for its strength-to-weight ratio, carbon fiber is often found in sports cars for body panels, roofs, and even structural components.
- Aluminum and Titanium: These materials are also favored for their lightweight properties and are commonly used in frames and trimmings.
Lighting Technology
Modern cool cars often employ cutting-edge lighting technology that enhances both functionality and aesthetics:
- LED Headlights: More energy-efficient and longer-lasting than traditional bulbs, LED headlights provide excellent road illumination.
- Adaptive Lighting: Some vehicles feature headlights that adjust the beam’s direction based on steering angle and speed to improve visibility around curves.
- Ambient Lighting: Externally, ambient lighting can accentuate design elements like grilles and contours, making the car more visually striking in low-light conditions.
Customization Options
Customization is a hallmark of cool cars, allowing owners to specify features that reflect their personal taste and style:
- Paint Options: Beyond standard color choices, custom paint jobs and effects like pearl or metallic finishes can make a car unique.
- Wheel Designs: Custom rims can dramatically change a vehicle’s appearance. Choices range from various sizes and finishes to innovative spoke designs.
- Decorative Accents: Features like chrome trim, customized badges, and decorative wraps add personal flair.
Functional Add-ons
Some cool cars also come with functional add-ons that enhance performance or practicality:
- Roof Racks and Spoilers: While often associated with sports cars, these features can also be adapted for everyday utility in some high-performance SUVs.
- Skid Plates and Bull Bars: For off-road or rugged vehicles, these add-ons protect against underbody damage and collisions with obstacles.
Interior Innovations
Inside, these cars offer luxury and technology. High-quality materials meet state-of-the-art infotainment systems. Comfort is paramount, with ergonomic seats and climate control.
The interior of cool cars is a showcase of innovation, comfort, and cutting-edge technology, designed to enhance both the driving experience and the aesthetic appeal. Here’s a detailed exploration of the various interior innovations typically found in cool cars:
Luxurious Materials
Cool cars often feature interiors crafted with high-quality, luxurious materials that elevate the comfort and sophistication of the cabin:
- Leather Upholstery: Premium leather is a common choice for seating, providing durability, comfort, and a plush feel.
- Alcantara®: Used on dashboard, door panels, and ceiling linings, Alcantara® offers a soft, suede-like finish that adds a luxurious touch.
- Carbon Fiber and Wood Accents: These materials are used for trim pieces and decorative inlays, combining modernity with classic elegance.
Advanced Seating Technology
Seating in cool cars is designed not only for comfort but also for ergonomic support during driving:
- Adjustable Bolstering: Seats in sports cars often feature adjustable side bolsters to provide better support during high-speed cornering.
- Massage and Ventilation Functions: For added comfort, especially in luxury models, seats might include massage functions and ventilation systems.
- Memory Settings: High-end cars often have memory settings for seats, allowing multiple drivers to save and quickly recall their preferred seating positions.
Cutting-Edge Infotainment Systems
The technology at the fingertips of drivers and passengers in cool cars is state-of-the-art, aimed at enhancing both usability and entertainment:
- Large Touchscreen Displays: Central consoles are typically dominated by large, responsive touchscreens that control media, navigation, and vehicle settings.
- Connectivity Features: Integration with smartphones, including apps, music streaming, and hands-free communication, is standard.
- Premium Sound Systems: High-fidelity audio systems from brands like Bang & Olufsen, Bose, or Bowers & Wilkins provide an immersive listening experience.
Innovative Dashboard Designs
Cool cars often feature innovative and visually appealing dashboard designs that merge functionality with futuristic aesthetics:
- Digital Instrument Clusters: Analog dials are frequently replaced by fully digital displays that can be customized to show various types of information.
- Heads-Up Displays (HUD): HUD technology projects important information, such as speed and navigation directions, directly onto the windshield.
- Ambient Lighting: Adjustable and multi-colored ambient lighting enhances the mood and character of the interior, often synchronized with driving modes or entertainment systems.
Climate Control and Environmental Comfort
Maintaining a comfortable cabin environment is crucial, and cool cars are equipped with advanced climate control systems:
- Multi-Zone Climate Systems: Individual climate settings allow passengers in different areas of the car to set their own preferred temperature.
- Air Quality Systems: Some vehicles include advanced filtration systems to ensure the air inside the cabin is clean, often with allergen filters and pollution sensors.
Safety and Assistance Features

Safety is paramount, and cool cars incorporate numerous advanced features to protect and assist drivers and passengers:
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Features like automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control enhance safety.
- Surround-View Cameras: These provide a 360-degree view around the car to aid in parking and maneuvering in tight spaces.
These interior innovations not only enhance the comfort and luxury of cool cars but also ensure that they are as enjoyable to ride in as they are to drive, blending advanced technology with exquisite craftsmanship to create a superior driving experience.
Performance and Engineering
Performance is a cornerstone for Cool:urriytflh98= Cars. They feature powerful engines and responsive handling. These cars are designed for both speed and efficiency.
Performance and engineering are key facets that define cool cars, setting them apart through superior capabilities and cutting-edge technology. Here’s a detailed look at the performance attributes and engineering innovations that make cool cars stand out:
Engine Power and Performance
Cool cars often boast powerful engines that deliver exceptional performance:
- High Horsepower Outputs: Many cool cars come equipped with engines producing high horsepower, enabling rapid acceleration and high top speeds.
- Turbocharging and Supercharging: These technologies are used to increase engine power without significantly increasing engine size, enhancing efficiency and power.
- Hybrid and Electric Engines: Some of the latest cool cars incorporate hybrid or fully electric engines, providing powerful torque and reduced emissions without compromising performance.
Transmission and Drivetrain
The transmission and drivetrain are crucial in delivering power effectively and efficiently from the engine to the wheels:
- Advanced Automatic Transmissions: Many modern cars use dual-clutch automatic transmissions that offer quick gear shifts and improved performance over traditional automatics. Some drivers opt for aftermarket upgrades, such as those offered by kwi clutching, a company specializing in clutches and clutch kits, to enhance their vehicle’s responsiveness and durability.
- Manual Transmission: Despite the rise of automatics, a traditional manual transmission is still favored in many sports cars for the control and driving engagement it offers.
- All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Systems: AWD systems improve traction and stability by distributing power to all four wheels, which is beneficial in both performance and harsh driving conditions.
Handling and Dynamics
The handling and dynamics of cool cars are engineered to provide a thrilling yet secure driving experience:
- Adaptive Suspension Systems: These systems adjust the damping characteristics in real-time to balance ride comfort and handling sharpness, depending on road conditions and driving style.
- Active Aerodynamics: Some cool cars feature active aerodynamic elements like spoilers and diffusers that adjust based on speed to optimize downforce and stability.
- Lightweight Construction: The use of lightweight materials like carbon fiber and aluminum in the chassis and body construction reduces weight, improving handling and efficiency.
Braking Systems
For high-performance cool cars, advanced braking systems are essential for safe deceleration and handling:
- Carbon Ceramic Brakes: Known for their durability and ability to withstand high temperatures with less fade, these brakes are often found in high-performance sports cars.
- Regenerative Braking: In electric and hybrid vehicles, regenerative braking helps in recapturing energy during braking, enhancing overall efficiency.
Technological Enhancements
Technology plays a significant role in enhancing the performance and driving experience:
- Launch Control: This feature optimizes engine and drivetrain settings for maximum acceleration from a standstill.
- Dynamic Driving Modes: Many cool cars offer selectable driving modes that alter settings for the engine, suspension, and even steering response to suit different driving conditions or preferences.
- Traction and Stability Control Systems: These systems help maintain vehicle control during acceleration and cornering, adjusting power output and braking to individual wheels as needed.
Safety and Performance Integration
Safety features in cool cars are designed not only to protect but also to enhance performance:
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): This is standard in many vehicles and helps to avoid skids and maintain control by detecting and reducing loss of traction.
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): Features like lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control not only contribute to safety but also enhance the driving experience by reducing the driver’s workload in certain conditions.
Through sophisticated engineering and advanced technology, cool cars provide an exhilarating driving experience that is both thrilling and safe, exemplifying the pinnacle of automotive performance and innovation.
Engine Specifications
cool:urriytflh98= cars are equipped with engines that provide thrilling acceleration. Turbocharged options are common, offering a perfect balance of power and fuel economy.
In cool cars, engine specifications are a critical component that defines their performance, efficiency, and appeal. These vehicles typically feature advanced and powerful engines designed to deliver outstanding driving dynamics. Here’s an in-depth look at the common engine specifications found in cool cars:
Engine Types and Layouts
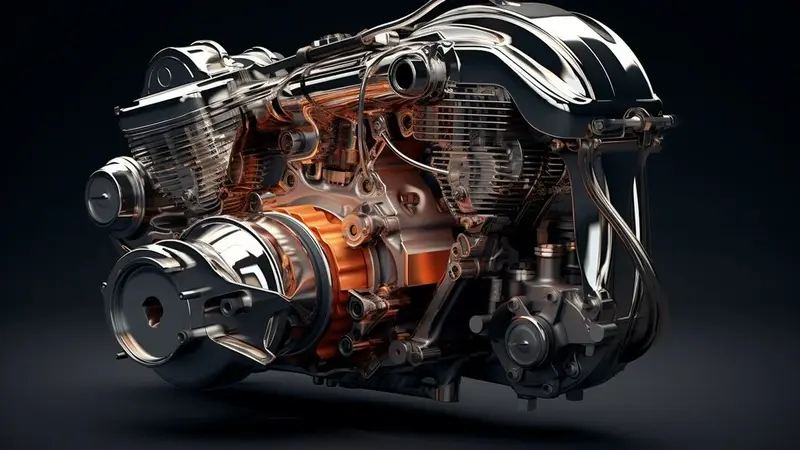
Cool cars can feature a variety of engine types and configurations, each offering unique benefits:
- V6 and V8 Engines: Popular in sports cars and luxury vehicles, these engines are prized for their power and the distinctive sound they produce.
- Inline-4 and Inline-6: These engines are known for their balance of efficiency and performance, often used in performance variants of standard models.
- Flat or Boxer Engines: Used in some sports cars, these engines have a lower center of gravity, improving handling by reducing body roll during cornering.
Displacement and Power Output
Engine displacement and power output are primary indicators of a car’s performance capabilities:
- High Displacement: Larger engines are often more powerful and capable of producing more torque, enhancing acceleration and top speed.
- Turbocharged and Supercharged: These technologies allow smaller engines to produce more power by increasing the amount of air and fuel that can be burned in the combustion chambers. This results in higher power outputs without the need for larger engines.
- Horsepower and Torque: Horsepower reflects the engine’s ability to perform over time, while torque indicates the immediate pulling power. Cool cars often boast high figures in both, ensuring rapid acceleration and robust performance.
Fuel System and Efficiency
Modern cool cars also focus on fuel efficiency and advanced fuel delivery systems:
- Direct Injection: This technology allows for more precise control of the fuel-air mixture that enters the engine, improving efficiency and power.
- Multi-Point Fuel Injection: Older but still effective, this system sprays fuel into the intake manifold, being replaced gradually by direct injection in newer models.
- Hybrid Technologies: Combining traditional internal combustion engines with electric motors, hybrid systems offer an excellent balance of power and efficiency, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
Engine Management and Tuning
Advanced electronics and software play a significant role in modern engine performance:
- ECU (Engine Control Unit): This computer regulates various engine functions, optimizing performance and fuel economy based on real-time data from sensors.
- Variable Valve Timing: Adjusting the timing of the valve openings and closings can improve performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions at different engine speeds.
- Cylinder Deactivation: In larger engines, some cylinders can be deactivated during light driving conditions to reduce fuel consumption without compromising performance.
Performance Enhancements
Many cool cars incorporate additional features that boost engine performance:
- Intercoolers: Used in turbocharged engines to cool the air entering the engine, increasing its density for better combustion.
- Performance Exhaust Systems: These not only enhance the sound of the car but also improve exhaust flow, which can increase power and efficiency.
- High-Performance Bearings and Pistons: Designed to withstand higher pressures and reduce friction, these components help in achieving higher performance and durability.
Through these sophisticated engine specifications, cool cars deliver an exhilarating driving experience, combining high power, advanced technology, and impressive efficiency. This makes them highly desirable among car enthusiasts and consumers looking for top-tier automotive performance.
Handling and Dynamics
Handling in these cars is precise, thanks to advanced suspension systems. Drivers enjoy a responsive and engaging driving experience. Safety features like anti-lock brakes and stability control enhance security.
Handling and dynamics are crucial elements that significantly influence the driving experience of cool cars, providing a blend of safety, control, and exhilaration. These aspects are engineered to deliver precise responses and stable performance, whether cruising on highways or navigating twisty roads. Here’s a detailed examination of what contributes to the superior handling and dynamics of cool cars:
Suspension Systems
The suspension system plays a pivotal role in handling by connecting the vehicle to its wheels and allowing for relative motion. In cool cars, advanced suspension technologies are employed:
- Adaptive Suspension: This system adjusts the damper settings in real time based on road conditions and driving behavior to balance ride comfort and handling precision.
- Active Suspension: More sophisticated than adaptive systems, active suspensions can control the movement of the wheels with actuators for optimal handling and comfort, virtually eliminating body roll during cornering.
- Magnetic Ride Control: Utilizing magnetorheological fluid in the shock absorbers, this technology adjusts the damping rate within milliseconds in response to changing road surfaces, enhancing both comfort and control.
Steering Systems
The steering system is another crucial factor in a car’s handling characteristics. Cool cars often feature innovative steering technologies:
- Electric Power Steering (EPS): This system replaces traditional hydraulic power steering with an electric motor, offering improved energy efficiency and adjustable steering responses.
- Dynamic Steering: Some systems can adjust the steering ratio based on speed and driving conditions, providing a quicker response at low speeds and more stability at high speeds.
- Rear-Wheel Steering: In some high-performance vehicles, the rear wheels can steer slightly to improve agility and stability during high-speed maneuvers and tight cornering.
Chassis and Body Structure
The design of the chassis and body also affects a vehicle’s handling:
- Rigid Body Structure: A stiff body shell provides a stable platform for mounting suspension components, which helps in maintaining precise wheel alignment during different driving conditions.
- Lightweight Materials: Using materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber, and high-strength steel reduces overall weight and improves the power-to-weight ratio, enhancing agility and acceleration.
- Aerodynamic Design: Aerodynamic features like spoilers, diffusers, and vented body panels help in reducing lift and drag, improving stability at high speeds.
Tires and Wheels
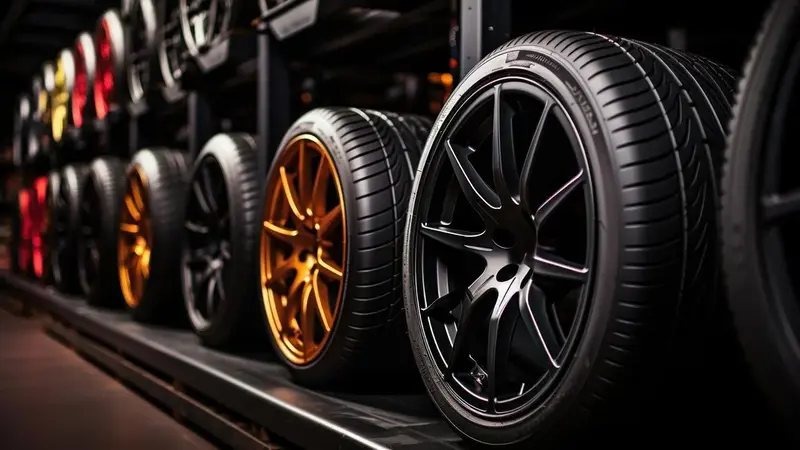

The choice of tires and wheels is integral to handling:
- High-Performance Tires: These are designed to provide better grip and traction on various surfaces, crucial for accelerating, braking, and cornering effectively.
- Wider Tires and Wheels: Increasing the width of the tires and wheels can offer a larger contact patch with the road, enhancing grip and stability.
- Wheel Alignment and Suspension Tuning: Proper alignment and tuning of the suspension can drastically affect handling, influencing factors like camber, toe, and caster angles.
Electronic Assistance Systems
Modern cool cars are equipped with various electronic systems to aid handling:
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): This system helps prevent skids and maintain control by detecting and reducing loss of traction.
- Traction Control Systems (TCS): TCS prevents wheel spin during acceleration by adjusting the power output to the wheels.
- Torque Vectoring: This technology improves cornering performance by distributing torque to specific wheels based on driving conditions, enhancing stability and agility.
Through these advanced engineering features, cool cars achieve a level of handling and dynamics that not only boosts the driving thrill but also ensures greater safety and control, making each drive a more engaging and enjoyable experience.
Technological Advancements
Cool= cars incorporate the latest in automotive technology. From autonomous driving features to electric powertrains, these cars are at the forefront of innovation.
Technological advancements in cool cars encompass a wide array of features and systems that elevate driving to new levels of efficiency, safety, and entertainment. Here’s an in-depth look at the key technological innovations commonly found in cool cars:
Autonomous and Semi-Autonomous Driving Features
Advances in autonomous driving technology are rapidly transforming the automotive landscape:
- Autopilot Systems: These allow the car to take over driving tasks such as steering, accelerating, and braking under certain conditions.
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): Features like adaptive cruise control, lane keeping assist, and automatic parking aid drivers in maintaining control and safety on the road.
Connectivity and Infotainment
Connectivity features in cool cars provide seamless integration with the digital world:
- Smartphone Integration: Systems like Apple CarPlay and Android Auto allow drivers to mirror their smartphone’s interface on the car’s display, enabling access to apps, navigation, and media.
- Wi-Fi Hotspots: Many cool cars offer built-in Wi-Fi hotspots, keeping passengers connected on the go.
- Advanced Navigation Systems: Real-time traffic updates, route suggestions, and even augmented reality features enhance navigation systems in cool cars.
Electrification and Hybrid Technology
The shift towards electrification is a significant trend in the automotive industry, with cool cars often at the forefront:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Fully electric cars are increasingly popular, offering high performance with zero emissions.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining electric motors with conventional engines, hybrids provide improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions without the range anxiety associated with fully electric vehicles.
- Regenerative Braking: This technology captures kinetic energy during braking and converts it into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery, enhancing efficiency.
User Interface and Controls
The user interface in cool cars is designed for ease of use and enhanced interaction:
- Digital Dashboards: Replacing traditional gauges and dials, digital dashboards offer customizable displays that provide drivers with a wealth of information about vehicle performance and conditions.
- Touchscreen Controls: Large, intuitive touchscreens control most of the car’s functions, from climate control to vehicle settings, reducing physical buttons and knobs.
- Voice Recognition: Advanced voice control systems understand and respond to natural language commands, allowing drivers to control various features without taking their hands off the wheel.
Safety Technologies
Safety remains a top priority, and technological advancements have significantly enhanced the protective features in vehicles:
- Collision Avoidance Systems: These systems detect potential collisions with other vehicles, pedestrians, or obstacles and can automatically apply the brakes to prevent or mitigate accidents.
- Blind Spot Detection: Sensors monitor areas around the vehicle that are difficult for the driver to see, alerting them to any hidden dangers when changing lanes or reversing.
- Night Vision and Enhanced Visibility: Using infrared cameras, night vision systems can detect objects beyond the reach of headlights, displayed on the dashboard screen to improve driving safety at night.
Performance Enhancements
Technological innovations also contribute to improving the performance of cool cars:
- Dynamic Performance Adjustment: Features like adaptive suspension, dynamic steering, and variable engine mapping allow the vehicle to adjust its performance characteristics based on driving conditions and driver inputs.
- Aerodynamic Adjustments: Active aerodynamics, such as retractable spoilers and adjustable air vents, optimize airflow over the vehicle to reduce drag and improve stability at high speeds.
These technological advancements not only make cool cars more enjoyable and safer to drive but also reflect the ongoing evolution of automotive capabilities, positioning these vehicles at the cutting edge of the industry.
Smart Features
Connectivity and smart features are integral to Cool= cars. They come equipped with systems that sync with mobile devices. Navigation, real-time traffic updates, and in-car entertainment are just a tap away.
Safety Technologies
Safety is not overlooked. These cars include advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Features such as automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assist protect passengers.
Safety technologies in cool cars have advanced significantly, integrating a variety of sophisticated systems that help prevent accidents and protect passengers. These features not only enhance the safety of the vehicle but also provide drivers with greater confidence on the road. Here’s an in-depth look at the key safety technologies commonly found in cool cars:
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
ADAS encompasses a broad range of features designed to enhance vehicle safety through automation and enhanced sensory information:
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): This system uses sensors to detect an imminent collision and can automatically apply the brakes if the driver does not respond in time, potentially avoiding or mitigating a crash.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): ACC automatically adjusts the car’s speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead, adapting to changing traffic conditions without driver input.
- Lane Keeping Assist (LKA): LKA helps prevent unintended lane departures by detecting lane markings and actively steering the car back into the lane if it begins to drift.
- Blind Spot Detection (BSD): This feature uses sensors on the sides of the vehicle to detect other vehicles in the driver’s blind spots, providing visual, auditory, or haptic alerts to prevent potential collisions during lane changes.
Collision Avoidance Systems
These systems are designed to reduce the likelihood of collisions through proactive measures:
- Forward Collision Warning (FCW): Using cameras and sensors, FCW alerts the driver to obstacles in the vehicle’s path, providing an early warning of potential collisions.
- Cross Traffic Alert: This feature helps drivers navigate out of parking spaces by warning of crossing traffic behind the vehicle, which is especially useful in busy parking lots or when the driver’s view is obstructed.
- Pedestrian Detection: Integrated with automatic braking systems, this technology detects pedestrians crossing in front of the vehicle and can initiate braking if a collision is imminent.
Visibility Enhancements
Improving the driver’s ability to see the road and surroundings is crucial for safe driving, particularly under challenging conditions:
- Adaptive Headlights: These headlights adjust their beam direction based on the steering angle and vehicle speed to better illuminate curves in the road ahead.
- Night Vision Systems: Employing infrared cameras, these systems help detect and display the presence of pedestrians, large animals, or other obstacles beyond the reach of conventional headlights.
- Rearview Cameras and Surround View Systems: Providing a 360-degree view around the vehicle, these systems help with parking and maneuvering in tight spaces, ensuring that drivers have a clear view of any obstacles.
Vehicle Stability and Control

Technologies designed to enhance the vehicle’s stability and handling play a crucial role in safety:
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): This technology helps prevent skids and maintain control by automatically applying brakes to individual wheels and reducing engine power if it detects loss of steering control.
- Traction Control Systems (TCS): TCS prevents wheel slip during acceleration by reducing engine power or applying brakes to individual wheels, ensuring better grip and stability.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during intense braking, maintaining the driver’s ability to steer and reducing stopping distances on slippery surfaces.
Passive Safety Features
In addition to active safety systems, cool cars are equipped with passive safety features that minimize injuries during accidents:
- Airbags: Modern vehicles are equipped with multiple airbags, including front, side, curtain, and knee airbags, which deploy in the event of a collision to protect occupants from impact forces.
- Crumple Zones: These are designed to absorb and dissipate energy during a collision, reducing the force transmitted to the occupants and protecting the vehicle’s structural integrity.
- Seatbelt Pretensioners: These automatically tighten seatbelts to secure passengers more firmly in the event of a crash, helping to reduce movement and the potential for injury.
Collectively, these safety technologies represent the cutting edge of automotive safety engineering, offering drivers and passengers unparalleled protection and peace of mind. As technology advances, these features become more sophisticated, further enhancing the safety profile of cool cars.
Environmental Impact
Cool= cars are designed with sustainability in mind. Many models feature hybrid or fully electric powertrains. These cars reduce emissions without sacrificing performance.
The environmental impact of cool cars is an increasingly critical aspect of automotive design and manufacturing, as consumer awareness and regulatory standards push the industry towards more sustainable practices. Here’s a detailed look at how cool cars are addressing environmental concerns through innovation and technology:
Fuel Efficiency and Emissions Reduction
Reducing fuel consumption and lowering emissions are primary objectives for modern vehicles to minimize their environmental footprint:
- Advanced Engine Technologies: Features like turbocharging, direct fuel injection, and variable valve timing improve the efficiency of combustion engines, leading to lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions.
- Lightweight Materials: Using materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber, and advanced composites in car construction reduces overall weight, which in turn requires less energy for movement, enhancing fuel efficiency.
- Aerodynamic Designs: Streamlined bodies that reduce air resistance can significantly improve fuel economy, which is critical for reducing emissions from gasoline-powered vehicles.
Electrification of Vehicles
Electrification is a major trend in reducing the environmental impact of vehicles:
- Hybrid Vehicles: Combining an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, hybrid cars can significantly reduce fuel consumption and emissions compared to conventional vehicles. They use regenerative braking and the engine to charge the battery, which then helps power the car.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Fully electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, which drastically reduces their environmental impact, especially when charged from renewable energy sources.
- Plug-In Hybrids (PHEVs): These vehicles have larger batteries than regular hybrids and can be charged externally, allowing them to drive longer distances on electric power alone, further reducing emissions.
Use of Sustainable Materials
The choice of materials used in vehicle manufacturing also affects the environmental impact:
- Recycled Materials: Many automakers are increasingly using recycled materials for interior components, including plastics, metals, and fabrics.
- Sustainable Production Methods: Some manufacturers focus on reducing waste and energy use in production processes, using renewable energy sources in their factories, and even implementing systems for capturing and reusing water.
- Biodegradable and Natural Materials: There is a growing trend towards using biodegradable materials and natural fibers like wool or flax for interior appointments, which are more environmentally friendly and reduce dependency on synthetic materials.
Emission Control Technologies
Vehicles are equipped with various systems designed to reduce harmful emissions:
- Catalytic Converters: These convert harmful gases like NOx, CO, and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances like nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
- Particulate Filters: Especially in diesel engines, these filters capture soot and other particulates from exhaust gases, significantly reducing air pollution.
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): This advanced emission control technology reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by injecting a urea solution into the exhaust stream, which converts NOx into nitrogen and water.
Lifecycle Impact
The overall environmental impact of a vehicle is not just about emissions during driving but includes the entire lifecycle from production to disposal:
- Manufacturing Impact: The production phase can contribute significantly to a car’s carbon footprint. Manufacturers are addressing this by optimizing production techniques and reducing resource consumption.
- Battery Disposal and Recycling: As the number of electric vehicles increases, the environmental impact of batteries becomes significant. Advances in battery technology and recycling methods are crucial for managing this impact.
- End-of-Life Vehicle Recycling: Recycling cars at the end of their life helps reduce waste and resource consumption. Automakers and recycling companies are working to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of recycling automotive materials.
Through these various approaches, cool cars are becoming more environmentally friendly, balancing performance and luxury with sustainability and reduced ecological impact. As technology progresses, the focus on reducing the environmental footprint of vehicles is expected to intensify, driven by both consumer demand and regulatory requirements.
Electric Powertrains
Electric cool:urriytflh98= cars offer a clean alternative to traditional engines. They provide instant torque and are incredibly quiet. Charging infrastructure is growing, making these cars more practical.
Electric powertrains are at the forefront of the automotive industry’s shift towards more sustainable, efficient, and environmentally friendly vehicles. This transition is driven by the need to reduce carbon emissions and minimize reliance on fossil fuels. Here’s an in-depth look at electric powertrains, highlighting their components, benefits, and the technological advancements that make them increasingly popular:
Key Components of Electric Powertrains
Electric powertrains differ significantly from traditional internal combustion engines. Here are the primary components:
- Electric Motor: The motor converts electrical energy stored in the battery into mechanical energy to drive the wheels. Unlike combustion engines, electric motors deliver torque almost instantaneously, providing quick acceleration.
- Battery Pack: The battery stores electrical energy used by the electric motor. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common, known for their high energy density and efficiency.
- Power Electronics Controller: This unit manages the flow of electrical energy between the battery and the electric motor, converting DC power stored in the battery to AC power used by the motor.
- Regenerative Braking System: Unlike conventional braking systems that dissipate kinetic energy as heat, regenerative braking systems recover this energy and convert it back into electricity to recharge the battery, enhancing the vehicle’s overall efficiency.
Benefits of Electric Powertrains
Electric powertrains offer several advantages over traditional combustion engines:
- Environmental Impact: Electric vehicles (EVs) produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution in urban environments.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric motors are typically more efficient than combustion engines in converting energy to power a vehicle, leading to better overall energy use.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline or diesel, and electric vehicles have fewer moving parts, resulting in lower maintenance costs.
- Performance Advantages: Electric motors provide higher torque at low speeds, improving the vehicle’s responsiveness and acceleration.
Technological Advancements in Electric Powertrains
The rapid development of technology in the field of electric powertrains is helping overcome previous limitations, such as range anxiety and high costs:
- Battery Technology Improvements: Advances in lithium-ion technology and the development of new materials like solid-state batteries are increasing energy density, reducing weight, and improving safety.
- Fast Charging Infrastructure: The development of fast-charging networks is addressing one of the main drawbacks of electric vehicles—extended charging times. Ultra-fast charging technologies can now recharge batteries to 80% in minutes.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: With the increase in renewable energy sources, electric vehicles can be charged using sustainable energy, further reducing their overall carbon footprint.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology: This innovative concept allows EVs not only to draw energy from the grid but also to feed electricity back into the grid when demand is high, potentially stabilizing energy prices and availability.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their benefits, electric powertrains face challenges such as high initial costs, concerns about battery life and disposal, and the need for a more extensive charging infrastructure. Continued investment in research and development is essential to enhance battery technology, decrease costs, and expand charging networks.
The future of electric powertrains looks promising, with ongoing advancements and increasing adoption rates. As governments around the world implement stricter emissions regulations and provide incentives for EV purchases, the shift towards electric mobility continues to accelerate, signaling a significant transformation in how vehicles are powered.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Manufacturers use sustainable materials in these cars. Recycled plastics and bio-based fabrics are common. This approach minimizes the environmental footprint of each vehicle.
The use of eco-friendly materials in the automotive industry is becoming increasingly important as manufacturers and consumers alike seek more sustainable practices. These materials are designed to reduce environmental impact through their production, use, and disposal processes. Here’s an in-depth look at the various types of eco-friendly materials used in cars, highlighting their benefits and applications:
Types of Eco-Friendly Materials
Recycled Plastics
Automotive manufacturers are increasingly utilizing recycled plastics for various components, such as dashboards, door panels, and seat fabrics. This not only reduces waste but also decreases the demand for virgin plastics, which involve petroleum in their production.
Natural Fibers
Natural fibers such as hemp, flax, kenaf, and bamboo are being used as alternatives to synthetic materials in car interiors and body components. These fibers are lightweight, strong, and have a much lower environmental footprint in terms of production and disposal compared to traditional automotive materials.
Biodegradable Materials
Some manufacturers are exploring the use of biodegradable materials for car interiors. These materials can decompose naturally at the end of their lifecycle, reducing landfill waste. Examples include bioplastics made from plant-based polymers.
Sustainable Leather and Alternatives
Leather production is resource-intensive and has significant environmental impacts. To address this, manufacturers are turning to sustainably sourced leather or alternatives like synthetic leather made from recycled materials or bio-based sources.
Benefits of Eco-Friendly Materials
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Eco-friendly materials typically require less energy to produce and generate fewer pollutants during their lifecycle compared to traditional automotive materials.
- Enhanced Sustainability: By using materials that are recyclable, biodegradable, or derived from renewable resources, the automotive industry can help conserve natural resources and reduce its ecological footprint.
- Innovation and Marketability: Incorporating eco-friendly materials is not only beneficial for the environment but also serves as a strong marketing tool in today’s eco-conscious market.
Technological Advancements and Applications
Lightweighting
Using materials such as natural fiber composites helps reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, which in turn improves fuel efficiency and reduces emissions, particularly important in both traditional and electric vehicles.
Sound Insulation
Natural fibers are effective at sound absorption and insulation. Replacing synthetic insulation materials with natural fibers can enhance passenger comfort while maintaining environmental benefits.
Durability and Aesthetics
Modern processing techniques have improved the durability, texture, and appearance of eco-friendly materials, making them more appealing and practical for automotive applications. Innovations in treatment and processing allow these materials to meet the rigorous standards required for automotive use.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the benefits of eco-friendly materials are clear, there are several challenges to their widespread adoption in the automotive industry:
- Cost: Eco-friendly materials can be more expensive to produce and process than traditional materials, although costs are decreasing as technology improves and scales up.
- Supply Chain and Availability: Developing a reliable supply chain for sustainable materials is crucial, as inconsistent supply can hinder production schedules and affect quality.
- Consumer Acceptance: Ensuring that eco-friendly materials meet consumer expectations in terms of performance, comfort, and aesthetics is vital for their adoption.
As technology advances and regulatory pressure to reduce environmental impacts increases, the use of eco-friendly materials in the automotive industry is expected to grow. This shift not only helps mitigate the environmental impact of vehicles but also aligns with global sustainability goals, paving the way for a greener future in automotive design and manufacturing.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
The demand for cool:urriytflh98= cars is influenced by changing consumer preferences. Buyers now seek vehicles that combine performance with environmental consciousness.
The automotive industry is witnessing significant shifts in market trends and consumer preferences, influenced by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and changing lifestyle needs. Understanding these trends is crucial for manufacturers and marketers to align their strategies accordingly. Here’s a detailed exploration of the current market trends and consumer preferences in the automotive sector:
Electrification and Sustainability
Consumers are increasingly aware of environmental issues, leading to a preference for more sustainable and eco-friendly vehicles:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): There’s a growing demand for EVs as consumers seek to reduce their carbon footprint. This is supported by government incentives, improvements in battery technology, and an expanding charging infrastructure.
- Hybrid Vehicles: Hybrids continue to be popular for those not ready to fully transition to electric but looking to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Sustainable Materials: There is an increased interest in vehicles that use recycled or biodegradable materials, reflecting broader concerns about sustainability.
Advanced Technology and Connectivity
Technology integration has become a key factor in purchasing decisions, with consumers expecting vehicles to keep pace with their connected lifestyles:
- Autonomous Features: While fully autonomous vehicles are still under development, semi-autonomous features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and automatic parking are highly sought after.
- Connected Services: In-car connectivity that allows for seamless integration with smartphones and access to real-time data, media streaming, and more is increasingly important to consumers.
- Safety Technologies: Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that enhance vehicle safety are becoming standard expectations, driving consumer choices.
Changing Ownership Models
The traditional model of car ownership is evolving, influenced by urbanization and the digitization of services:
- Subscription Services: cool:urriytflh98= cars subscription services offer a flexible alternative to ownership or leasing, appealing to those who prefer not to commit to a single vehicle or deal with maintenance issues.
- Ride-Sharing and Mobility as a Service (MaaS): Urban consumers are increasingly relying on ride-sharing services. This trend is complemented by MaaS, which integrates various forms of transport services into a single accessible on-demand service.
Preference for Utility and Versatility
Vehicles that offer versatility and enhanced utility are in demand, reflecting changes in consumer lifestyles and family needs:
- SUVs and Crossovers: These vehicles remain popular due to their higher seating capacity, more cargo space, and the perception of increased safety. Their versatility makes them suitable for both urban and off-road conditions.
-
Luxury and Personalization
Even in a market leaning towards practicality and sustainability, there is a robust segment that values luxury and personalized experiences:
- High-End Features: Consumers are willing to invest in luxury brands that offer exclusive design, superior comfort, and bespoke customization options.
- Performance Vehicles: Despite the shift towards sustainability, there is a steady demand for high-performance sports cars among enthusiasts who value power and driving dynamics.
Economic Influences
Economic factors play a significant role in shaping consumer preferences in the automotive market:
- Cost Sensitivity: Economic uncertainty influences consumers to prioritize value for money, fuel efficiency, and lower maintenance costs.
- Incentives and Regulations: Governmental policies and incentives to encourage the purchase of eco-friendly vehicles significantly impact consumer preferences and market trends.
Understanding these trends helps automotive companies innovate and adapt to meet the evolving needs of consumers. As the industry continues to evolve, staying ahead of these trends will be crucial for automotive brands aiming to maintain or increase their market share in a competitive environment.
Popularity Among Young Buyers
Younger demographics are drawn to cool:urriytflh98= cars. They appreciate the blend of technology, style, and eco-friendliness. Social media and influencer endorsements have also boosted their popularity.
Understanding these preferences is crucial for automotive brands aiming to attract this demographic. Here’s an in-depth look at why certain vehicles are popular among young buyers:
Affordability and Value
Young buyers often have budget constraints, making affordability a key factor in their purchasing decisions:
- Cost-Effective Models: Vehicles that offer good value for money, including lower initial purchase prices and cost-effective maintenance, tend to attract young buyers.
- Financing and Leasing Options: Flexible financing options, such as lower interest rates or attractive leasing deals, can make higher-priced vehicles more accessible to younger consumers.
Technology and Connectivity
Technology is a significant part of daily life for younger generations, and they expect their vehicles to reflect this:
- Smartphone Integration: Features like Apple CarPlay and Android Auto, which allow for seamless integration of smartphone functionalities with the car’s infotainment system, are particularly appealing.
- Advanced Infotainment Systems: Large touchscreens, voice commands, and robust infotainment systems that support streaming services and provide real-time updates are highly valued.
- Internet Connectivity: In-car Wi-Fi hotspots that keep the driver and passengers connected are an attractive feature for tech-savvy young buyers.
Environmental Concerns
Many young buyers are environmentally conscious, influencing their preference for eco-friendly vehicles:
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (EVs): There is a growing trend among young buyers to opt for hybrids or EVs as concerns about carbon footprints and sustainable living increase.
- Fuel Efficiency: Even in non-hybrid and non-EV choices, young buyers prioritize fuel efficiency to reduce both their environmental impact and fuel costs.
Style and Personalization
Young buyers often see their vehicle as an extension of their personality, which influences their choices:
- Modern Design: Stylish, sleek, and modern designs that stand out are more likely to attract young buyers. This demographic tends to favor cars that make a statement.
- Customization Options: The ability to personalize a car, whether through exterior colors, interior finishes, or additional packages, is a significant draw.
Safety and Reliability
Safety Features: Advanced safety features like automatic emergency braking, lane departure warnings, and driver-assist technologies are important to young buyers who value both innovation and safety.
- Reliability: Young buyers want cars that are not only affordable but reliable.
Urban Suitability
Many young buyers live in urban environments, so they look for vehicles that fit this lifestyle:
- Compact Size: Smaller vehicles that are easier to maneuver and park in tight city spaces are popular among young urban dwellers.
- Eco-Friendly Public Image: Young buyers often prefer cars that project a socially responsible image, aligning with urban trends towards sustainability.
Understanding these factors can help automotive brands tailor their products and marketing strategies to appeal to young buyers, who are increasingly looking for vehicles that combine affordability, technology, style, and sustainability. As this demographic’s purchasing power grows, their preferences will continue to shape the automotive market’s future trends.
Impact on the Automotive Industry
Cool:urriytflh98= Cars are setting trends in the automotive industry. They push other manufacturers to innovate in design, performance, and sustainability.
From the surge in electric vehicles (EVs) to the integration of advanced digital technologies, the industry is undergoing transformative changes. Here’s a detailed analysis of how these trends are impacting the automotive industry:
-
Integration of Autonomous Technologies
Autonomous driving technologies are progressing rapidly, influencing several aspects of the automotive industry:
- Safety and Regulation: The development and integration of autonomous features necessitate rigorous testing and new regulatory frameworks to ensure safety.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Many traditional automakers are partnering with tech companies and startups to leverage their expertise in software and artificial intelligence, essential for advancing autonomous technologies.
- Consumer Acceptance: While the technology is advancing, the industry faces the challenge of building consumer trust and understanding regarding the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles.
Advanced Connectivity and Infotainment Systems
As digital connectivity becomes a standard expectation among consumers, its influence is notable:
- In-car Experience: There is an increased focus on enhancing the in-car user experience through sophisticated infotainment systems that offer seamless integration with mobile devices, high-speed internet connectivity, and interactive interfaces.
- Data Security and Privacy: With cars becoming more connected, issues of data security and user privacy are more prominent. Automakers must address these concerns by implementing robust cybersecurity measures.
- New Revenue Streams: Connected services open new avenues for revenue, including subscription-based models for premium content, software updates, and enhanced functionalities.
Changes in Consumer Behavior and Market Dynamics
The automotive industry must adapt to shifts in consumer behavior and expectations:
- Demand for Personalization: Consumers increasingly expect options to customize their vehicles, not just in terms of aesthetics but also in functionality and driving experience. This trend pushes automakers to offer a broader range of options and packages.
- Urban and Shared Mobility: The rise of urbanization and the sharing economy affects vehicle ownership trends. There is growing interest in car-sharing services and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS), which may decrease individual car ownership in favor of shared and on-demand vehicle services.
Economic and Supply Chain Implications
Global economic shifts and supply chain dynamics also play crucial roles:
- Global Supply Chain Complexity: The automotive industry is experiencing challenges related to the global supply chain, such as disruptions in the delivery of semiconductor chips, which are crucial for modern vehicles. These disruptions can lead to production delays and increased costs.
- Local Production Incentives: To mitigate supply chain risks and respond to local market needs, automakers are increasingly considering regional production strategies and nearshoring components.
These impacts signify a period of significant transition and opportunity within the automotive industry. Companies that can adapt swiftly and effectively to these new realities—embracing technological innovation, adjusting to changing consumer preferences, and navigating regulatory environments—are likely to thrive in the evolving automotive landscape.
Conclusion
cool:urriytflh98= cars offer an exciting glimpse into the future of automobiles. They merge impeccable design with groundbreaking technology. For car enthusiasts and eco-conscious buyers, these vehicles provide a thrilling yet responsible choice. As technology advances, cool:urriytflh98= cars will continue to evolve and inspire the automotive world.
he automotive industry is undergoing a transformative phase marked by significant shifts in technology, consumer preferences, and regulatory landscapes. The surge in electric and hybrid vehicles is reshaping manufacturing processes, driving research and development, and necessitating new infrastructures. Similarly, the advent of autonomous driving technologies is not only enhancing vehicle capabilities but also prompting collaborations between traditional automakers and tech companies, while raising important safety and regulatory concerns.
Connectivity and advanced infotainment systems are becoming staples in modern vehicles, enhancing the driving experience but also introducing challenges related to data security.
The industry’s response to these trends includes embracing eco-friendly materials, investing in sustainable technologies, and adapting to new consumer expectations about vehicle functionality and ownership models. As automakers navigate these changes, the ability to innovate in alignment with global sustainability goals, technological advancements, and shifting consumer demands will determine their success in a competitive marketplace.
This dynamic era in the automotive industry promises exciting opportunities for innovation and growth but requires manufacturers to remain flexible and responsive to an ever-changing global landscape.
